Brain tumor
"Laboratory plasma tests can be used for patients who, due to the tumour’s inaccessible location or the patient’s highly deteriorated general condition, cannot undergo surgery”.
DR. JAIME GÁLLEGO
COORDINATOR. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TUMORS AREA

What is a brain tumour?
A brain tumour is a growth of cancer cells in the central nervous tissue (the main component of the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord).
A brain tumour can be primary or metastatic. Primary brain tumours originate in the cells of the brain structure itself, whereas metastatic tumours are tumours that have spread to the brain from an extracerebral location.
Research has shown that the survival or cure rate of brain tumours depends, to a large extent, on the total removal of the tumour.
In the Central Nervous System Tumors Area of the Cancer Center Clínica Universidad de Navarra we have extensive experience in the treatment of brain tumors.
We are pioneers in clinical trials and techniques, as well as in immunotherapy for the treatment of glioblastoma or the use of fluorescent microscopy to achieve extraordinary rates of complete removal of malignant glioma.

A PERSONALIZED MEDICINE
Second Opinion,
peace of mind
Request a second opinion from our professionals with great experience in the diagnosis and treatment of oncological diseases
In 3 days, without leaving home.
Symptoms of a brain tumour
Headache
This is the most common symptom, although non-specific. It may not be enough on its own to suspect the presence of a brain tumour.
Drowsiness
May indicate increased intracranial pressure, a more indicative sign in cases of gliomas.
Loss of strength
This is usually a focal symptom that depends on the location of the tumour, affecting limbs or half of the body.
Neurological deficits
Includes alterations such as slurred speech, visual field problems and other specific neurological signs depending on the area affected.
Seizures
May be an initial manifestation of the tumour, especially in certain brain locations.
Brain haemorrhage
In some cases, the presence of a tumour can trigger bleeding, causing sudden and severe symptoms.
Do you have any of these symptoms?
If you suspect that you have any of the above symptoms,
you should consult a medical specialist for a diagnosis.
What are the causes of a brain tumour?
There is no known cause responsible for the occurrence of malignant brain tumours. Less than 5% of gliomas have a known family history. On the other hand, there are several degenerative brain diseases that predispose to gliomas.
Frequent use of mobile phones has also not been shown to cause a higher incidence of these brain tumours.
What is the prognosis of brain tumours?
The prognosis depends mainly on the aggressiveness of the tumour. In adults, 60% of primary brain tumours are gliomas or astrocytomas, with low-grade I and II gliomas.
Low-grade gliomas I and II. Good prognostic factors are being under 40 years of age, tumour diameter less than 6 cm, tumour not exceeding the midline, histological type oligoastrocytoma and absence of neurological deficits. Survival in these patients with high-grade tumours ranges from 9 to 2 years depending on the prognostic group.
Gliomas III and IV: Good prognostic factors are age (under 40-50 years), good general condition with autonomy, normal mental status and complete surgical resection. Survival in these patients with high-grade tumours ranges from 2 years to 6 months depending on the prognostic group.
How is the brain tumour diagnosed?
Diagnosis of the brain tumour is based on advanced imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which detects the lesion, its size and location, and PET with methionine, which helps to pinpoint the type of tumour.
To confirm the diagnosis, a biopsy is performed by open surgery or image-guided puncture, a stereotactic technique that reduces discomfort for the patient. In addition, molecular analysis of the tissue obtained in the operating theatre and laboratory allows the type and grade of the tumour to be accurately determined.
Treatment of brain tumours
The Clínica Universidad de Navarra has a fluorescent microscope, a new technique which allows for the total removal of the tumor in more than 80% of the cases.
The objectives of surgery for brain tumors are
- An exact and precise diagnosis of the tumor.
- Decrease the pressure on the healthy brain to improve symptoms.
- Total removal can cure the tumor or facilitate the effect of other treatments.
- Removal without damaging healthy bordering areas.
Neurophysiological monitoring in the operating room
It helps to determine whether or not the surgery can continue through an area without producing a sequel to the patient. It increases the removal and decreases the complications.
Intraoperative image-guided surgery
For all tumors, the image from the previous MRI is used as a map for a navigator to help the surgeon.
Chemotherapy aims at destroying the tumor cell.
In the case of brain tumors, there are two important characteristics that make it more difficult to administer chemotherapy:
- The blood-brain barrier, which protects the central nervous system from the arrival of toxic substances from the blood.
- The special resistance of these tumors to current chemotherapy drugs.
The chemotherapy treatment applied depends on the type of brain tumor. Chemotherapy has been shown to be effective in prolonging survival in high-grade gliomas.
Chemotherapy is the treatment of choice in most patients with primary lymphomas of the central nervous system, after biopsy confirmation of the diagnosis.
In brain tumors that occur in children, chemotherapy treatment is essential, as they are more sensitive to these drugs.
Despite all the treatments, in many cases chemotherapy does not manage to stop the progression of the disease. Therefore, it is important to continue research with basic research and clinical trials.
Precision in the planning and execution of radiation therapy is essential to ensure that the maximum dose is given to the tumor while preserving and not damaging normal tissues.
In the Clinic, this precision is possible, since we have qualified professionals with extensive experience and the most advanced technology in imaging tests for a correct and careful planning.
Radiation therapy can also be curative in some benign tumors, especially if their size and location allows a high enough radiation to the tumor volume.
Studies have shown that its administration in the postoperative period does not increase the survival of these patients, but increases the time in which the tumor is controlled.
La Clínica is the only Spanish center that carries out a study for the treatment of glioblastomas with immunotherapy. The new therapy, which is administered to participating patients in the form of vaccines, is combined with standard first-line treatment. It consists of the surgical removal of the tumor, followed by the administration of radiotherapy and chemotherapy with temozolomide.
The immune system is critical in the development and control of tumors. Immunotherapy aims to repair or increase the response of the patient's immune system.
The limited amount of disease and the combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy make this a good added option to the treatment of patients with glioblastoma.
What clinical trials do we have on brain tumors?
Proton Therapy
Unit
The Clinica has the most advanced Proton Therapy Unit in Europe at its headquarters in Madrid.
Proton therapy provides very promising results with minimal side effects in pediatric tumours, and those of the skull base, brain, head and neck.
It incorporates, for the first time in Europe, a Hitachi device, that is present in academic medical centres of international reference.
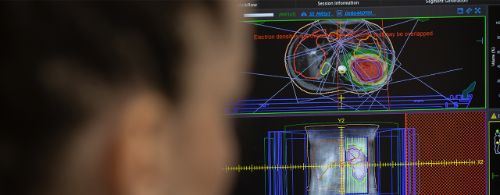
MR Linac
MRI-guided radiation therapy
MR Linac is an advanced radiotherapy technology that combines a linear accelerator with an integrated 1.5 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging system, with high diagnostic accuracy before, during and after treatment.
MR Linac technology allows real-time adaptive radiotherapy to be administered, which adapts the dose and precision of the radiotherapy administered to the patient according to the specific characteristics of each person and each tumor.
Central Nervous System Tumors Area
of the Cancer Center Clínica Universidad de Navarra
In the Central Nervous System Tumors Area we offer maximum safety and efficiency in brain tumor surgery, being the first hospital with a high field magnetic resonance within the operating room.
We have a highly specialized team in the surgery of brain tumors, with more than 15 years of experience.
The individualized treatment of each case by an interdisciplinary team allows us to offer the best alternative to each patient.

Why at the Clinica?
- Integral evaluation of the patient.
- Cutting edge technology.
- Expert professionals who are a national reference.
Our expert brain tumour team
Learn all about cancer and its latest treatments
‘The present and future of cancer treatment is based on highly specialised teams’
Dr. Antonio González, director of the Cancer Center of the Clínica Universidad de Navarra, summarises what cancer is, causes, diagnosis, treatment and innovative advances in the future of cancer treatment.




























